OLE DB Command Transformation in SSIS
How To Use OLE DB Command Transformation [ Delete Rows in Data Flow Task]
Scenario:
We have a SQL table which contains our data. Every day we get a text file from our users
and they want to delete records from SQL table those match with the text file records those they have provided.
The records in text file are less than 50 all the time and
we are not allowed to create any staging table for this new process.
and they want to delete records from SQL table those match with the text file records those they have provided.
The records in text file are less than 50 all the time and
we are not allowed to create any staging table for this new process.
Solution:
If we could load the data into a staging table and then write Delete statement by joining two tables
that would be better solution(set based queries).
As we do not have option to create table and we have to handle everything in Data Flow task.
We will be using OLE DB Command Transformation to do the job for us.
OLE DB Command Transformation will perform row by row operation but in our case it will be OK
as number of rows are always going to be less than 50. If you have a lot of deletes/updates, insert that
data into some staging table and use set base queries in Execute SQL task to do the job.
that would be better solution(set based queries).
As we do not have option to create table and we have to handle everything in Data Flow task.
We will be using OLE DB Command Transformation to do the job for us.
OLE DB Command Transformation will perform row by row operation but in our case it will be OK
as number of rows are always going to be less than 50. If you have a lot of deletes/updates, insert that
data into some staging table and use set base queries in Execute SQL task to do the job.
Here is our solution for deleting few records on daily basis from SQL Table by matching records from text file.
Step 1:
Create a table with data by using below Query
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[DestinationTable](
[CountryName] [varchar](50) NULL,
[SalePersonName] [varchar](50) NULL
)
GO
insert into [dbo].[DestinationTable]
Select *
FROM (
SELECT N'uSA' AS [countryname], N'aamir shahzad' AS [salepersonname] UNION ALL
SELECT N'Italy' AS [countryname], N'andy' AS [salepersonname] UNION ALL
SELECT N'UsA' AS [countryname], N'Mike' AS [salepersonname] UNION ALL
SELECT N'brazil' AS [countryname], N'Sara' AS [salepersonname] UNION ALL
SELECT N'INdia' AS [countryname], N'Neha' AS [salepersonname] UNION ALL
SELECT N'Brazil' AS [countryname], N'Anna' AS [salepersonname] UNION ALL
SELECT N'Mexico' AS [countryname], N'Anthony' AS [salepersonname] ) t;
Step 2:
Create SSIS Package. After create SSIS Package, Create Flat File Connection and use below data in text file
CountryName,SalePersonName,SaleAmount
USA,aamir shahzad
Italy,andy
Step 3:
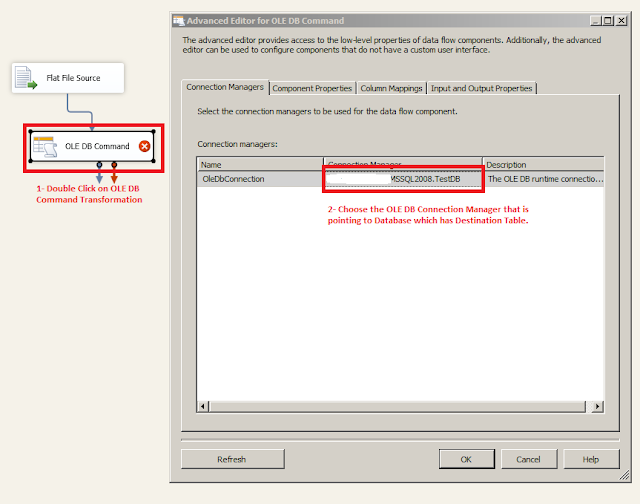
Bring OLE DB Command Transformation to Data Flow pane and connect your Flat File Source to it. After that do configure as shown by blow snapshots.
Choose the OLE DB Connection which is point to Database which has Destination table
Write the query as shown below.
Delete from dbo.DestinationTable where countryName=?
AND SalePErsonName=?
Map the input columns to the parameters as shown below, Remember our query we have provided CountryName first in query so we have to map to param_0 and then SalePersonName to param_1
Final Output:
As we can see in the snapshot, before running a package we had 7 records. After running package two records were deleted and only 5 records left in destination table.